Differences Between Solar Cables and Ordinary Cables?
In daily life, cables silently bear the heavy responsibility of power transmission. Whether it's the normal operation of household appliances, the humming of factory machinery, or the dazzling lights of a city at night, the contribution of cables is indispensable. In fact, the cables used in different scenarios vary significantly. Take solar cables and ordinary cables, for example; the differences between them are considerable.
The conductor, as the "core lifeline" of the cable, has its material selection directly impacting the cable's conductivity. Ordinary cables typically use copper or aluminum conductors, which can stably transmit electrical energy in general indoor environments, meeting daily electricity needs. For example, many of the wires in our homes are copper-core conductors, which are relatively affordable and provide stable power support for various appliances. Solar cables, however, use more sophisticated conductor materials, mostly high-purity oxygen-free copper, and some even use multi-strand soft copper wire. This high-purity conductor material has extremely low resistivity and excellent conductivity, minimizing energy loss during transmission. Furthermore, to further enhance the performance of solar cables in complex environments, their conductors are often tinned. Tinning significantly improves the conductor's oxidation resistance and corrosion resistance, like giving the conductor a strong "protective armor." For example, in solar power plants near the sea, the humid air and salt in the seawater have a strong corrosive effect on cables, but tinned solar cable conductors can effectively resist this corrosion, ensuring the long-term stable operation of the cables.
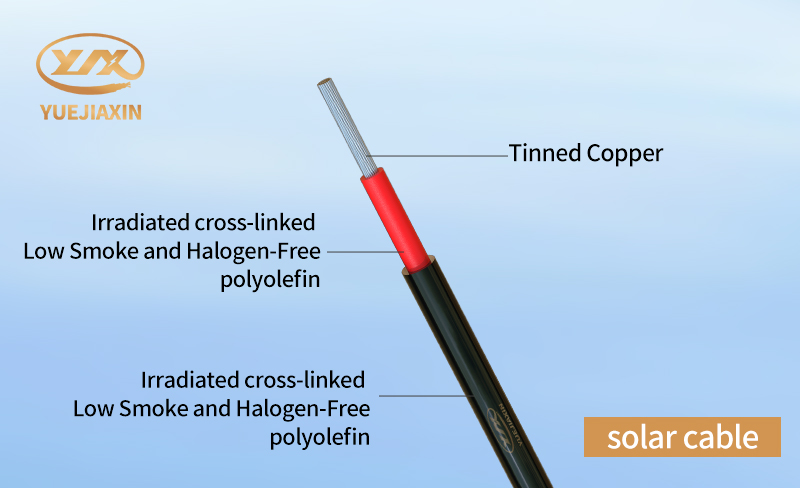
Insulating materials act as the "safety guardians" of cables, playing a crucial role in isolating conductors from the external environment and preventing electrical leakage and short circuits. The main insulating materials used in ordinary cables are polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE). PVC insulation is inexpensive and easy to process, making it widely used in applications such as household wiring. However, PVC materials have relatively poor temperature resistance and can only operate stably in environments not exceeding 70°C. If this type of ordinary PVC-insulated cable is placed in a high-temperature outdoor environment, its performance will rapidly deteriorate, and the insulation layer may soften, deform, or even lose its insulating effect, leading to safety hazards. Solar cables, on the other hand, use a more advanced irradiated cross-linked polyolefin as their insulating material. This material undergoes a special irradiation cross-linking treatment. Under irradiation, its molecular structure undergoes a remarkable transformation, forming a more stable and compact network structure. This unique structure gives it many excellent properties and prevents it from aging as easily as ordinary insulating materials. It is these superior properties that enable the insulating material of solar cables to provide long-term, reliable insulation protection for conductors in harsh outdoor environments, ensuring the stable operation of solar systems.
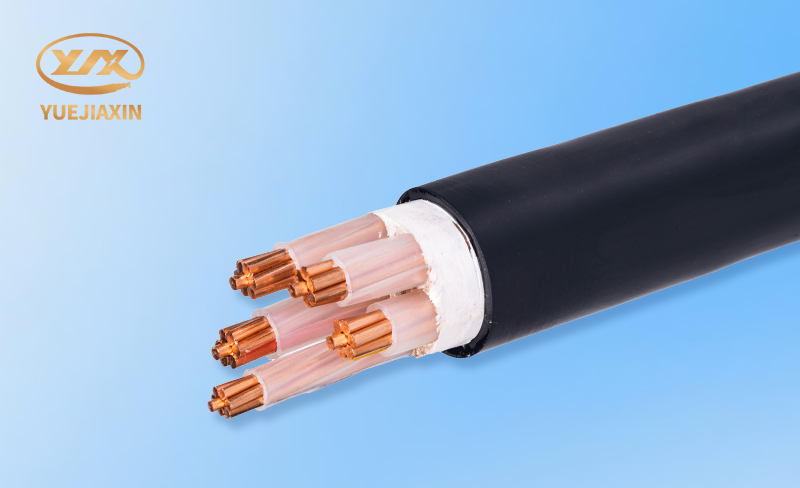
In practical applications, we cannot simply judge which type of cable is better; instead, we must choose the appropriate cable based on specific needs and usage scenarios. Only in this way can we ensure that the cables work stably and efficiently in their respective roles, providing reliable power support for our lives and production.
- PVC-Insulated Cable
- 450/750V BV Single- Core Cu/PVC Cable
- 450/750V BVR Single- Core Cu/PVC Cable
- 300/500V Or 450/750V RV Single-Core Cu/PVC Flexible Cable
- 300/500V Or 450/750V RVV Multi-Core Cu/PVC/PVC Flexible Black Cable
- 300/500V Or 450/750V RVV Multi-Core Cu/PVC/PVC Flexible White Cable
- 300/500V Or 450/750V RVVP Multi-Core Cu/PVC/CWS/PVC Screened Flexible Cable
- 450/750V KVV Multi-Core Cu/PVC/PVC Control Cable
- 450/750V KVV22 Multi-Core Cu/PVC/STA/PVC Armoured Control Cable
- 450/750V KVVP Multi-Core Cu/PVC/CWS/PVC Screened Control Cable
- 450/750V KVVP2-22 Multi-Core Cu/PVC/CTS/STA/PVC Screened Armoured Control Cable
- 0.6/1KV PVC-Insulated PVC-sheathed Single-Core Power Cable
- 0.6/1KV PVC-Insulated PVC-sheathed Multi-Core Power Cable




