the difference between RVV and RV
In daily life, we're often overwhelmed by the dazzling array of cable products. If you're not careful, you might end up buying the wrong cable, even though it looks similar. For example, RVV and RV cables differ by only one letter, but misusing them can cause unnecessary trouble.
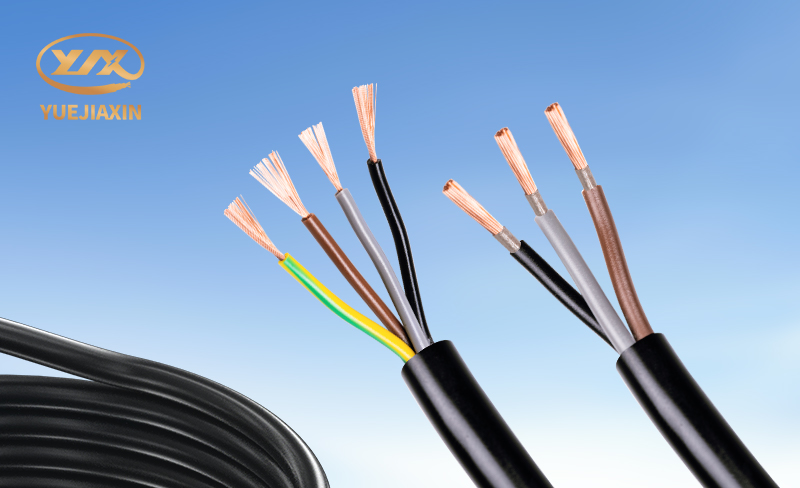
RV stands for Copper Core PVC Insulated Flexible Connecting Cable. The "R" here stands for "flexible wire," indicating that the conductor is made of multiple strands of fine copper wire, making it soft and flexible, like a small rope. The "V" stands for PVC insulation, which provides excellent insulation and ensures electrical safety. Simply put, it's a flexible wire with PVC insulation. Let's take a look at RVV, which stands for Copper Core PVC Insulated PVC Sheathed Flexible Cable. The "R" also indicates "flexible wire," the first "V" stands for PVC insulation, and the second "V" stands for PVC sheath. As the name suggests, it has an additional PVC sheath compared to RV, like an extra protective jacket for the wire.
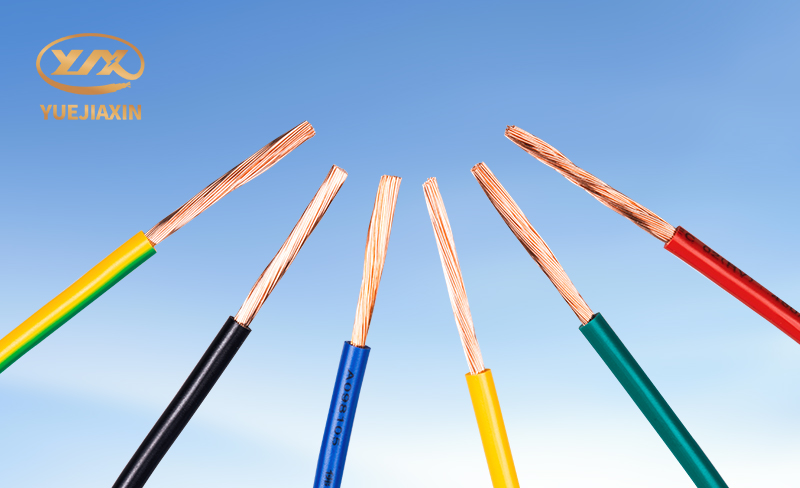

What are the core differences between RVV and RV? RV is a single-core flexible cable made from multiple strands of fine copper wire. This structure makes it flexible and allows for easy maneuvering in complex wiring environments with frequent bends and twists, such as those inside electrical cabinets. RVV, on the other hand, is a multi-core flexible cable. It's like a "large family," consisting of two or more RV cables that are integrated together to transmit power or signals. RV cables are relatively simple, lacking a sheath and featuring only a single layer of polyvinyl chloride insulation, which exposes them to direct environmental contact. This requires extreme care during use to avoid damage. RVV cables, on the other hand, have an additional PVC sheath, acting like a sturdy armor, protecting the core from mechanical damage and chemical attack, such as corrosive gases and liquids. It also provides a certain degree of flame retardancy, significantly improving safety. RV cables are rated at 450V/750V, meaning they operate stably and safely within a voltage range of 450V to 750V. They are suitable for applications requiring higher voltages and can withstand large voltage fluctuations, ensuring proper equipment operation. RVV cables, on the other hand, are rated at a relatively low voltage of 300V/500V, making them more suitable for weak current systems with less stringent voltage requirements. They provide stable power and signal transmission, meeting operational requirements. RV cables come in a variety of colors, including red, yellow, white, blue, green, brown, gray, and black. These colors serve as a convenient identifier, making it easier for workers to distinguish between different lines. This allows for easier identification during wiring and maintenance, significantly improving efficiency and reducing the risk of errors. RVV cables, while typically available in black and white, are relatively simple colors, but they are sufficient for identification and use in specific applications.
When purchasing cables, it's crucial to first clarify your needs and select the appropriate cable based on your specific usage scenarios and electrical requirements.
The power of brand cannot be underestimated. Choosing a reputable brand with guaranteed quality is like providing a safeguard for electrical safety. When purchasing, be sure to check the product's certifications and test reports.
The cable's appearance can also provide a glimpse into its quality. First, look at the core. High-quality cores should be made of high-purity copper, exhibit a uniform, bright purple-red color, and have a dense, pore-free cross-section. Repeated hand bending of the copper wire should make it feel flexible and resilient, resisting breakage. Low-quality cores may appear dark or whitish, with visible impurities or black oxidation spots on the cross-section. They may feel stiff and prone to breaking. Next, consider the sheathing. For RVV cables, the sheathing should be uniform in thickness, clearly printed, and durable, resisting tearing. High-quality cables have bright, uniform colors on the insulation and sheathing, while low-quality products may be duller or even exhibit color variations.
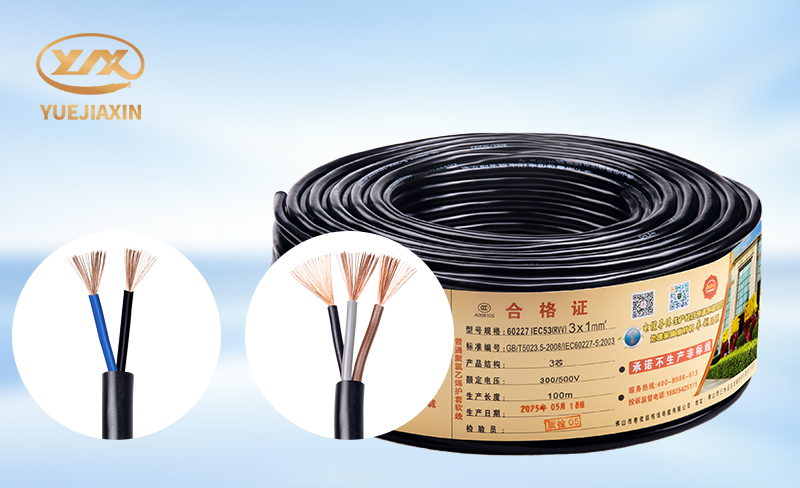

Although RV and RVV have similar names, in terms of structure, RV is a single-core soft cable, while RVV is a multi-core flexible cable with an additional sheath. They also differ in electrical performance, rated voltage, and appearance, color. RV is primarily used for industrial power distribution, while RVV is widely used in appliances, security, and other fields. When purchasing, be sure to choose reputable brands with guaranteed quality based on your specific needs, and pay attention to the cable's appearance.




